South- East Asia |
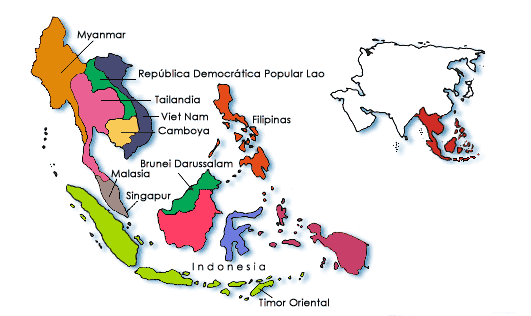
South- East Asia |

|
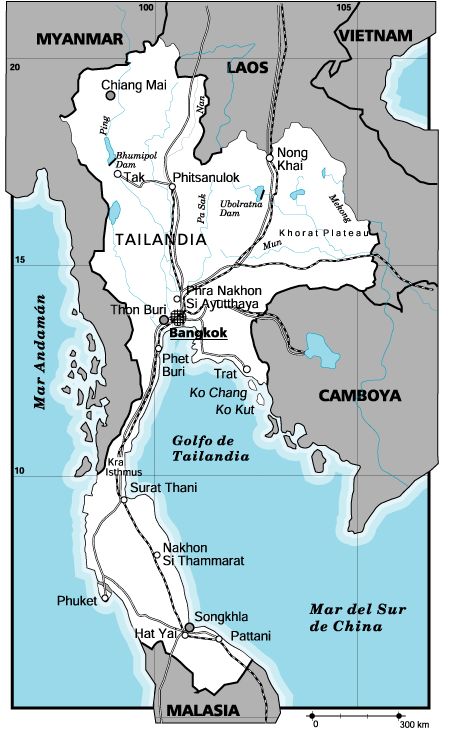
Thailand
 |
Population: 64.316.134 inhabitants
Area: 513.120 Km2 Coin: Baht PIB: 8.678 $ per capita Language: Thai and English Official name: Muang Thai, or Prathet Thai (Kingdom of Thailand). Capital: Bangkok (Krung Thep) 6.355.144 inhabitants (2000). Other cities: Thon Buri 115.500 inhabitants; Ratchasima 207.500; Chiang Mai 170.300; Khon Kaen 143.200; Nakhon Pathom 122.500 (2000). Government: Kingdom Religion: Buddhism (official, 94%); Muslims, reunited in the South, are over the 4%. There are a Christian and Hindu minority. Geography. Thailand is located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula. There are mountain areas at the North and West, from where the rivers Ping and Nan descended to a central plain. These rivers flow into the Thailand Gulf through broad deltas. The plain is very fertile, with very fertile rice fields. The Southern region occupies part of the peninsula of Malaca. The widespread deforestation suffered in the area has produced a decrease in the production of wood and rubber, which has forced the native population to emigrate. |
|
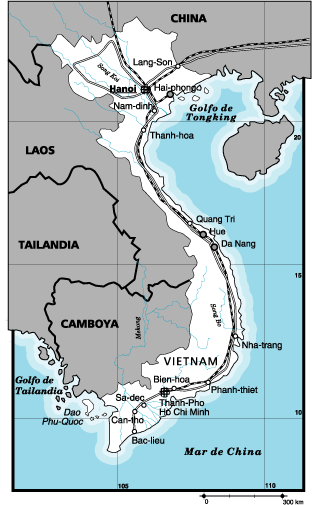
Vietnam
 |
Population: 88.537.271 inhabitants
Area: 329.560 Km2 Coin: Dong PIB: 3.071 $ per capita Language: Vietnamese Official name: Nu'ó'c Công Hòa Xâ Hôi Chu' Nghî’a Viêt Nam. Capital: Hanoi 3.977.000 inhabitants (2003). Other cities: Ho Chi Minh (called Saigon), 5.566.900 inhabitants.; Haiphong 1.763.300; Da-Nang 762.800 (2000). Government: Presidential. Religion: mostly Buddhist and traditional cults. There are over 2 millions of Catholics and over 3 millions of followers of the hoa-hao y cao-dai sects. Geography: Vietnam is a narrow and long country, placed at the Eastern coast of the Indochina peninsula, over the Tongkin gulf and the Southern Chinese Sea. Of rainy tropical climate, it is placed in the monsoon winds’ area. It has jungle vegetation and its hydrographycal network is very well developed. The North area is the highest. Two rivers which flows in the shape of a delta stand up: the Song Koi at North and the Mekong at the South. Agriculture is the traditional occupation, and rice is its main product. The North of the country is rich in anthracite, lignite, coal, iron, manganese, bauxite and titanium. The main industries are mining, food stuff and textile articles. |
|
Philippines

|
Population: 89.651.082 inhabitants
Area: 300.000 Km2 Coin: Filipino peso PIB: 5.137 $ per capita Language: Filipino and English Name official: Republika ñg Pilipinas. Capital: Manila 10.352.000 inhabitants (2003). Other cities: Cebu 1.172.800 inhabitants; Davao 1.145.600; Bacolod 739.600; Cagayan 407.800; Zamboanga 147.200 (2000). Government: Presidential Republic. Religion: Catholics, 83%; Filipino Independent Church, 3%; Muslims, 5%; Protestants, 5%; Animists and Buddhists and others, 4%. Geography: Philippine archipelago is formed by 7.107 islands, although 11 of them span the 94% of the total area and concentrate most of the population. The archipelago is located around 100 kms. Southeast Asia. It is surrounded by the Filipino Sea (at East), the South China Sea (at West), the Celebes Sea(at South). Luzon and Mindanao are the most important areas. Of volcanic origin, the archipelago is part of the “Pacific Ring of Fire” Its topography is mountainous, with large coastal plains suitable for agriculture: sugar, rice, hemp, copra, tobacco. The weather is wet and tropical. Temperatures used to be around 26,5° C. Filipinos know three seasons: tag-init o tag-araw (summer, since March to May), tag-ulan (rain season, since June until November) and tag-lamig (cold season, since December to February). Heavy rainfall favour the growth of tropical jungles. It is also the main Southeast Asian producer of iron, and it has petroleum, chromium, copper, nickel, cobalt, silver and gold. |
1. Write the correct country: Thailand, Vietnam or Philipines: